-
Latest
 Oct 26
Oct 26
Bio-Specimen Sample Collection and Processing: A Comprehensive Guide
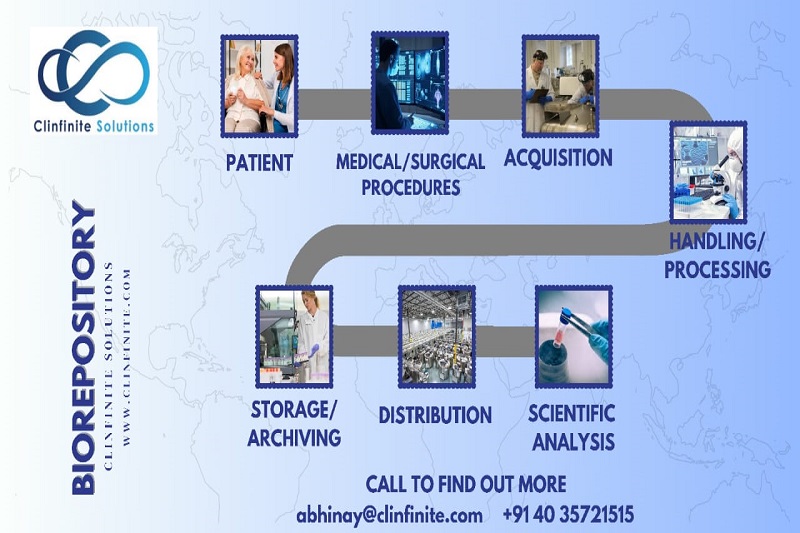
Bio-specimen samples are biological materials, such as blood, urine, saliva, tissue, and cells that are collected from humans or animals for research or diagnostic purposes. The accurate collection and processing of bio-specimen samples is essential to ensure the quality and reliability of the results obtained from subsequent analyses.
-
 Sep 22
Sep 22
Explain the Meaning of Biobanking and Its Importance
Biobanking, a word gaining popularity in scientific fields, is at the forefront of revolutionary research and medicinal advancements. This article looks into the complexities of biobanking, its historical evolution, the various types of biobanks, the essential processes involved, and its vital role in defining the future of medical research.
The collecting, storage, and processing of biological samples for research purposes is known as biobanking. Blood, tissue, DNA, RNA, and even living cells can be used as samples. Biobanks are essentially archives for these precious resources, which are made available to scientists researching a wide range of diseases and health situations. -
Latest
 Sep 14
Sep 14
FFPE and Frozen Biospecimen Samples
FFPE (Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded) and frozen biospecimen samples are vital resources in medical research. FFPE samples involve preserving tissues in formaldehyde, followed by embedding in paraffin wax, making them suitable for long-term storage. These samples are advantageous for retrospective studies, as they retain structural integrity.
On the other hand, frozen biospecimen samples are snap-frozen and maintained at ultra-low temperatures. This method preserves biomolecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins, making them ideal for molecular analysis. However, frozen samples may degrade over time, requiring stringent storage conditions.
Researchers choose between FFPE and frozen samples based on their specific research goals. FFPE offers histological insights, while frozen samples are preferred for molecular investigations. Both sample types are invaluable in advancing our understanding of diseases and developing diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.

Your Research & Development Partner
ICH-GCP Compliant CRO
Clinical Development Solutions
Learn More Contact Us
Your Research & Development Partner
ICH-GCP Compliant CRO
Bio-Specimen & Bio-Repository Solutions
Learn More Contact Us
Your Research & Development Partner
ICH-GCP Compliant CRO
Biometrics Solutions
Learn More Contact Us


